Neuro Topics - Parkinson’s disease
SEARCH OTHER RESEARCH AREAS
October 24, 2024
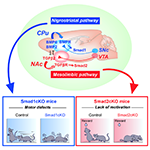
New research in mice from Pascal Kaeser, Nao Uchida, and colleagues, first authors Xintong Cai and Changliang Liuexplains why levodopa, a drug commonly used to treat Parkinson's Disease, works to alleviate some symptoms but not others.
Original article in: Nature >
September 13, 2024
A new study from Trisha S. Pasricha and Subhash Kulkarni, first author Jocelyn Chang (Tufts) finds that the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease was 76 percent higher among those with damage to the lining of their upper gastrointestinal tract than among those without.
Original article in: JAMA Open Network >
September 13, 2024
New research in lab models from Stephen Gomperts and colleagues, first author K. N. Rose, indicates that low doses of carbon monoxide — comparable to that experienced by smokers — protected against neurodegeneration and prevented the accumulation of a key Parkinson’s-associated protein in the brain.
Original article in: NPJ Parkinson's Disease >
August 29, 2024
Technological advances allow scientists to more rapidly create in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease using stem cells, in ways that could provide more personalized diagnostic and treatment methods. From Vikram Khurana and colleagues, co-first authors Isabel Lam and Alain Ndayisaba.
Original article in: Neuron >
April 15, 2024
Deep brain stimulation is a powerful therapeutic approach for severe brain circuit dysfunctions that can effectively alleviate the heterogeneous symptoms characteristic of Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, Tourette’s syndrome, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Barbara Hollunder (Lab of Andreas Horn) explains what invasive brain stimulation can teach us about the circuit architecture of the brain’s dysfunction — and which commonalities it shares with a prism.
Original article in: Nature Neuroscience >
March 27, 2024
A simple skin biopsy test has shown a high accuracy rate in detecting an abnormal form of alpha-synuclein, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease, according to neurologists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Original article in: American Medical Association >
February 2, 2024
Harvard Medical School researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Wyss Institute have developed a molecular test that successfully detected and quantified telltale protein clumps in tissue and fluid samples obtained from patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Original article in: PNAS >
February 2, 2024
Researchers from Harvard and Boston University have used a soft, wearable robot to help a person living with Parkinson’s walk without freezing. When individuals with Parkinson’s disease freeze, they suddenly lose the ability to move their feet, often mid-stride, resulting in a series of staccato stutter steps that get shorter until the person stops altogether. These episodes are one of the biggest contributors to falls among people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Original article in: Nature Medicine >
October 6, 2023
Akiko Terauchi and Hisashi Umemori share new research that identified the pathway-specific signals that establish functionally segregated dopaminergic synaptic connections in the mammalian brain. The findings may provide strategies to treat pathway-specific disease symptoms in diseases like Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and depression, by targeting the pathway-specific molecular signals.
Original article in: Cell >
July 26, 2022
Erinc Hallacli and colleagues in Vikram Khurana’s lab show a new function of Parkinson’s Disease protein alpha-synuclein in modulating Processing Bodies, cellular hubs for mRNA control. The work has physiologic and therapeutic implications for the delicate balance between lipid biology and RNA homeostasis in the cell dictated by alpha-synuclein.
Original article in: Cell >
August 10, 2020
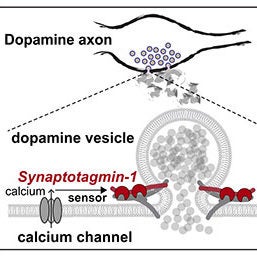
Aditi Banerjee shares new research from the lab of Pascal Kaeser demonstrating that Synaptotagmin-1 acts as the fast calcium sensor to support dopamine release.
Original article in: eLife >
July 21, 2020
Jeffrey Schweitzer shares a new study demonstrating the advantages of the personalized cell therapy approach for Parkinson’s disease and potentially for other degenerative diseases of the nervous system.
Original article in: New England Journal of Medicine >
February 12, 2020
HMS News article on new research from the labs of Paolo Bonato and colleagues suggesting that wearable technology and other mobile data-gathering devices should replace self-reporting diaries to track symptoms in people with Parkinson’s disease.
Original article in: Nature Partners Journal Digital Medicine >
June 28, 2019
Digital devices can interfere with everything from sleep to creativity
Original article in: Nature Partners Journal Digital Medicine >
June 28, 2019
How one species of bacteria consumes the primary treatment for Parkinson’s disease could reveal more about how the microbiome impacts our health.
Original article in: Science >