Neuro Topics - Gut-Brain Interactions
SEARCH OTHER RESEARCH AREAS
September 13, 2024
A new study from Trisha S. Pasricha and Subhash Kulkarni, first author Jocelyn Chang (Tufts) finds that the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease was 76 percent higher among those with damage to the lining of their upper gastrointestinal tract than among those without.
Original article in: JAMA Open Network >
July 18, 2024
Boston Children's Hospital Answers profiles the research of clinician-scientists Tamar Katz and Kinga Tomczak, studying potential differences in the microbiomes of individuals with these disorders.
June 11, 2024
New research finds that gas released by some gut bacteria stimulates other gut bacteria to produce a hormone involved in pregnancy and in an FDA-approved treatment for postpartum depression.
Original article in: Cell >
August 30, 2023
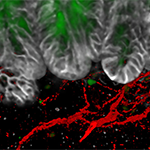
HMS News article on new research from David Ginty and colleagues, first author Rachel L. Wolfson, defining five types of colon neurons that are specialized for sending different signals to the brain. These findings may eventually lead to the development of better therapies for a variety of gastrointestinal problems.
Original article in: Cell >
May 11, 2023
Brigham and Women's Hospital press release on new research from Laura D Kubzansky, Yang-Yu Liu, and colleagues, first author Shanlin Ke, linking specific bacteria in the gut to positive emotions like happiness and hopefulness and healthier emotion management skills. Also featured in the Harvard Gazette.
Original article in: Psychological Medicine >
November 28, 2022
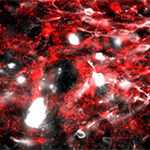
HMS News article on new research from Isaac Chiu and colleagues, first author Daping Yang, illuminating how pain neurons shield the gut from damage.
Original article in: Cell >
June 30, 2022
HMS News profiling PiNBAC, a new post-bac program that seeks to increase diversity in neuroscience by providing research experience and professional development to college graduates from underrepresented groups. PiNBAC is led by Tari Tan and Bob Datta of the Dept of Neurobiology at HMS.
June 30, 2022
HMS News article on new research from Stephen Liberles and colleagues, first author Chuchu Zhang, using mice to describe how different cell types in the brain work together to suppress nausea.
Original article in: Cell Reports >
July 13, 2021
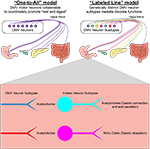
Ken Tao and Brad Lowell share a new study characterizing vagal motor neurons that innervate the digestive system. This work demonstrates a labeled-line model of the vagus motor nerve where genetically-defined subtypes of vagal motor neurons project to specific regions of the digestive system and engage neurochemically-distinct subtypes of enteric neurons.
Original article in: Neuron >
June 4, 2021
Harvard Gazette Q+A with David R. Williams on the mental and physical tolls discrimination take on Black lives and what individuals can do to help mitigate them.
June 4, 2021
Harvard Gazette article profiling the research of Deirdre Barrett into how our dreams have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
June 4, 2021
Harvard Gazette article on new research from a collaboration of more than 50 international scientists finding that Neanderthals and ancient humans adapted to eating starch-rich foods as far back as 100,000 years ago.
Original article in: PNAS >
July 10, 2020
Alexandra Vaccaro and Yosef Kaplan Dor describe new research from the labs of Dragana Rogulja and Mike Greenberg identifying the gut as a major site of impact when sleep is severely suppressed.
Original article in: eLife >
May 13, 2020
Harvard Gazette article on new research from the lab of Kevin Eggan, first author Aaron Burberry, identifying a gut-brain connection in mice with a common ALS genetic mutation.
Original article in: Nature >
December 19, 2019
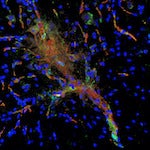
HMS News article on new research from the lab of Isaac Chiu and colleagues, first author Nicole Y. Lai, demonstrating in mice that the nervous system is able to detect and actively defend against Salmonella.
Original article in: Cell >
June 28, 2019
Digital devices can interfere with everything from sleep to creativity
June 28, 2019
How one species of bacteria consumes the primary treatment for Parkinson’s disease could reveal more about how the microbiome impacts our health.
Original article in: Science >