Neuro Topics - Schizophrenia
SEARCH OTHER RESEARCH AREAS
August 1, 2024
Complement proteins are known to mediate the pruning of synapses by microglia. In new work with implications for our understanding of schizophrenia, Krishna K. Narayanan, Matthew L Baum, Matthew Johnson, and Beth Stevens, and colleagues at Boston Children's Hospital, find that a neuronal protein called CSDM1 opposes the deposition of complement proteins on synapses, making them less vulnerable to engulfment by microglia.
March 14, 2024
Brain tissue samples from people with schizophrenia and from older adults have strikingly similar sets of changes in gene activity in two types of brain cells, suggesting a common biological basis for the cognitive impairment often seen in people with schizophrenia and in older people, according to new research from Steve McCarroll, Sabina Berretta, and colleagues. First author Emi Ling.
Original article in: Nature >
October 6, 2023
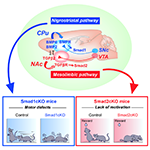
Akiko Terauchi and Hisashi Umemori share new research that identified the pathway-specific signals that establish functionally segregated dopaminergic synaptic connections in the mammalian brain. The findings may provide strategies to treat pathway-specific disease symptoms in diseases like Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and depression, by targeting the pathway-specific molecular signals.
Original article in: Cell >
Disease Characteristics of Dopaminergic Neurons in Neurodevelopmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
July 20, 2021
Maria Sundberg shares new research from the lab of Mustafa Sahin on the role of a small piece of chromosome 16, called the 16p11.2 locus, in disease phenotypes of dopaminergic neurons. The team identified that RhoA pathway activation led to network dysfunction in 16p11.2 deletion neurons. Its inhibitor, Rhosin, rescued the hyperactivity of these neuronal networks. In the future, the RhoA pathway and its inhibitors may serve as potential therapeutic targets.
Original article in: Nature Communications >
March 10, 2021
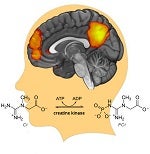
Xiaopeng Song from the lab of Fei Du at McLean Hospital shares new human brain imaging work revealing that an impairment in energy production may underlie the problems in functional neural connectivity observed in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Original article in: Molecular Psychiatry >
March 9, 2021
Harvard Gazette article on a recent Facebook Live event "The Coronavirus Pandemic: Grieving and Mental Health". This article highlights the work of Christy Denckla, a postdoc at the Broad Institute and Harvard T.H. Chan School, whose research focuses on resilience following exposure to trauma.
Original article in: Molecular Psychiatry >
March 9, 2021
Round up of awards and honors earned by the HBI community.
Original article in: Molecular Psychiatry >
October 21, 2020
HMS News article on how new research into a newly discovered primate brain cell type could improve studies on neuropsychiatric disease. From the labs of Stephen McCarroll, Guoping Feng, Gordon Fishell, Sabina Berretta, Leslie Kean, Chris Walsh and several others, first author Fenna Krienen.
Original article in: Nature >
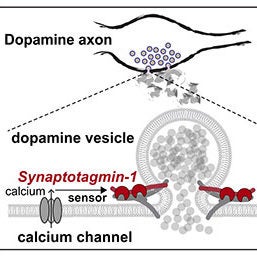
August 10, 2020
Aditi Banerjee shares new research from the lab of Pascal Kaeser demonstrating that Synaptotagmin-1 acts as the fast calcium sensor to support dopamine release.
Original article in: eLife >
May 11, 2020
HMS News article on new research from the labs of Steven McCarroll and colleagues, first author Nolan Kamitaki, pinpointing genes underlying sex biases in autoimmune disorders and schizophrenia.
Original article in: Nature >
July 3, 2019
McLean's Deborah Levy and colleagues provide a proof-of-principle demonstration of symptom relief by targeting a specific genotype and links an individual structural mutation to the pathophysiology of psychosis and treatment response.
Original article in: Biological Psychiatry >
January 29, 2019
Harvard Gazette article highlighting a large international genetic study from the teams of Michael Weedon (University of Exeter), Richa Saxena (MGH), and colleagues (co-lead authors Samuel Jones and Jacqueline Lane), shedding new light on the body clock and its links to mental health.
Original article in: Nature Communications >