Featured Story:
Rethinking How We Train Scientists for Today’s Careers
February 24, 2026
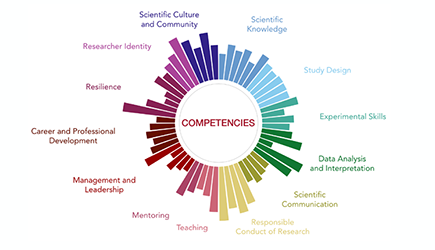
How do we prepare early-career scientists for today’s wide range of paths in and beyond the lab? Jelena Patrnogić shares a new flexible competency framework she developed with Xiuqi Li and David Van Vactor that makes expectations clearer for trainees, mentors, and programs, and supports growth across both research and professional skills.
Community Stories
February 3, 2026
iPSC-derived sensory neurons provide an accessible platform for scientists to study sensory biology and disease; however, these cells are similar to embryonic neurons. Chelsey Derderian-LeBlang and Rosalind Segal present a protocol to accelerate the maturation of iPSC-derived sensory neurons, by providing external signals from satellite glial cells. They show that satellite glia, while previously described as a support cell, play a major role in both sensory neuron development and degeneration.
Original article in: Stem Cell Reports >
January 14, 2026
New experiences trigger rapid changes in gene activity and DNA accessibility in the brain’s memory-center, the hippocampus. Lisa Traunmüller and Erin Duffy describe new research from the Greenberg lab that uses advanced sequencing to map how different hippocampal regions respond at the molecular level to a novel environment — revealing how experiences shape brain circuits that underlie learning and memory.
Original article in: Nature Communications >
October 31, 2025
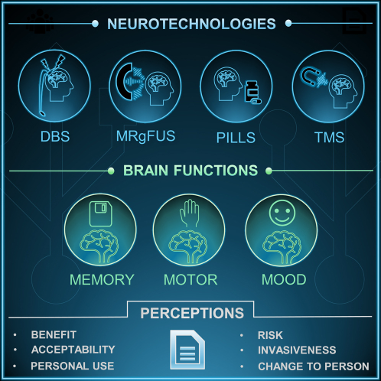
Rémy Furrer and Amanda Merner share the results of a survey of 1,052 U.S. adults, which found that neurotechnologies targeting motor symptoms were viewed as more acceptable and beneficial than those for mood or memory symptoms. Non-surgical options like transcranial magnetic stimulation were generally preferred over invasive ones such as deep brain stimulation.
Original article in: Device >
August 20, 2025
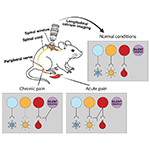
New research reveals that acute and chronic insults both reshape how pain signals are sent to the brain, but through distinct mechanisms. By using long-term calcium imaging in mice, researchers from the Woolf lab tracked the same spinal cord neurons over time and found that acute pain temporarily increases sensitivity, while chronic nerve injury recruits a previously ‘silent’ group of neurons – offering a potential key to understanding chronic pain.
Original article in: Neuron >
In the News
February 4, 2026
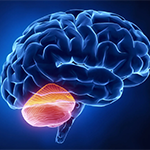
New research from Evelina Fedorenko and colleagues, first author Colton Casto, identifies specific language-processing regions in the cerebellum that closely mirror regions in the frontal and temporal lobes of the neocortex, the brain areas long understood as the specialized epicenter for processing language.
Original article in: Neuron >
February 4, 2026
New research from from Chana A. Sacks, Zirui Song, and colleagues, first author George Karandinos, analyzing records from a large health insurance database finds that in the year following a parent’s injury, children had increases in psychiatric diagnoses and mental health visits, especially if the parent had suffered a severe injury.
Original article in: New England Journal of Medicine >
February 4, 2026
The Harvard Gazette profiles the research of Bruce Yanker and the importance of his teams' groundbreaking research showing that lithium is a natural, biologically important element in the brain that has the potential to prevent or even reverse Alzheimer’s disease.
Awards & Honors
December 3, 2025
Round up of awards and honors earned by the HBI community.
November 10, 2025
Round up of awards and honors earned by the HBI community.