HOME / FOR EVERYONE / PHOTOS / 2018 Beauty of the Brain Image Contest
We are excited to share with you the images submitted to us for the 2018 HBI “Beauty of the Brain” image contest. Five winning images were selected, and each winner will receive $200 and a customized desk plaque with their image. Thank you to everyone who participated!
Hair Cells and Neurons of the Cochlea
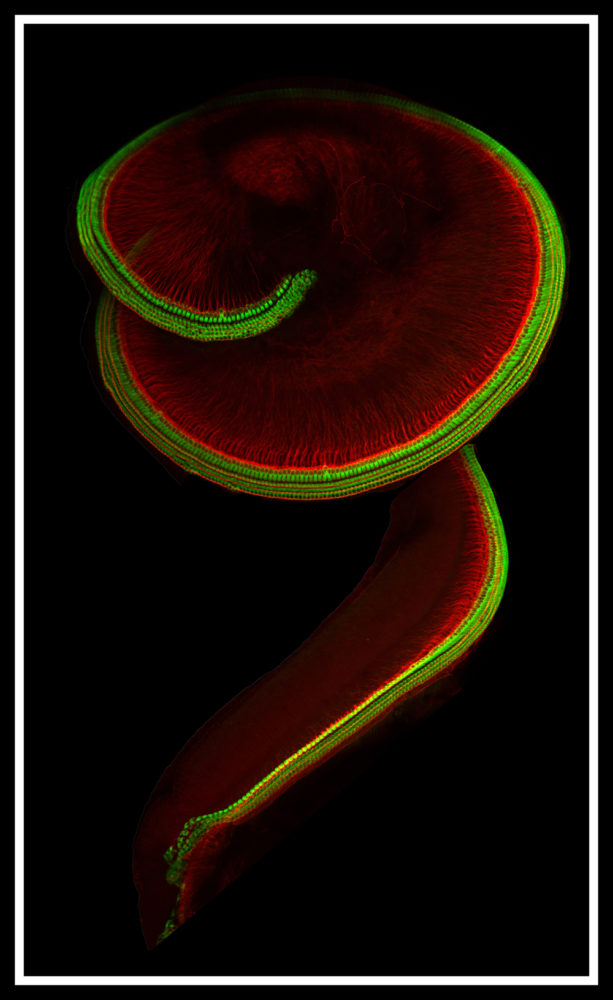
Submitted by: Carl Nist-Lund and Bifeng Pan
Lab of Jeff Holt and Gwenaelle Geleoc
Winner of 2018 HBI “Beauty of the Brain” Image Contest
This is the inner ear cochlea from a 6-day-old mouse. Over 3,000 specialized cells responsible for hearing are highlighted in green, and the neurons that transmit this information to the brain are highlighted in red.
Neuronal Network Cultured on an Integrated Circuit Chip
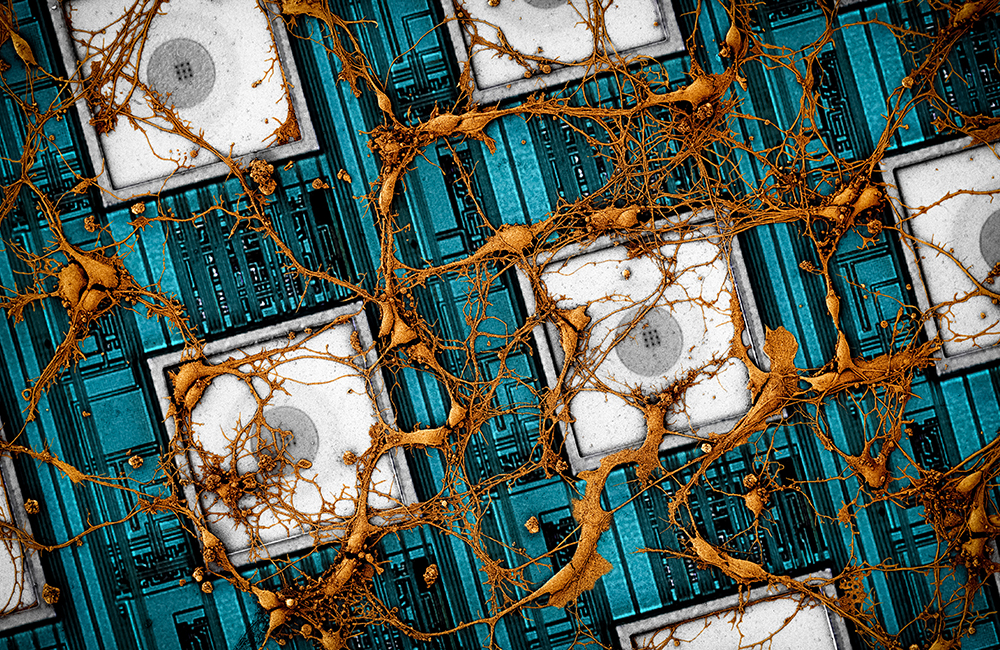
Submitted by: Jeffrey Abbott and Tianyang Ye
Labs of Hongkun Park and Donhee Ham
Winner of 2018 HBI “Beauty of the Brain” Image Contest
The electronic integrated circuit in combination with post-fabricated nanoscale electrodes creates a high-fidelity electronic interface to neurons cultured on its surface. The device’s capability to intracellularly record and stimulate the neurons across its thousands of pixels enables large-scale neuronal networks to be measured and manipulated
Blood Vessels in the Developing Retina
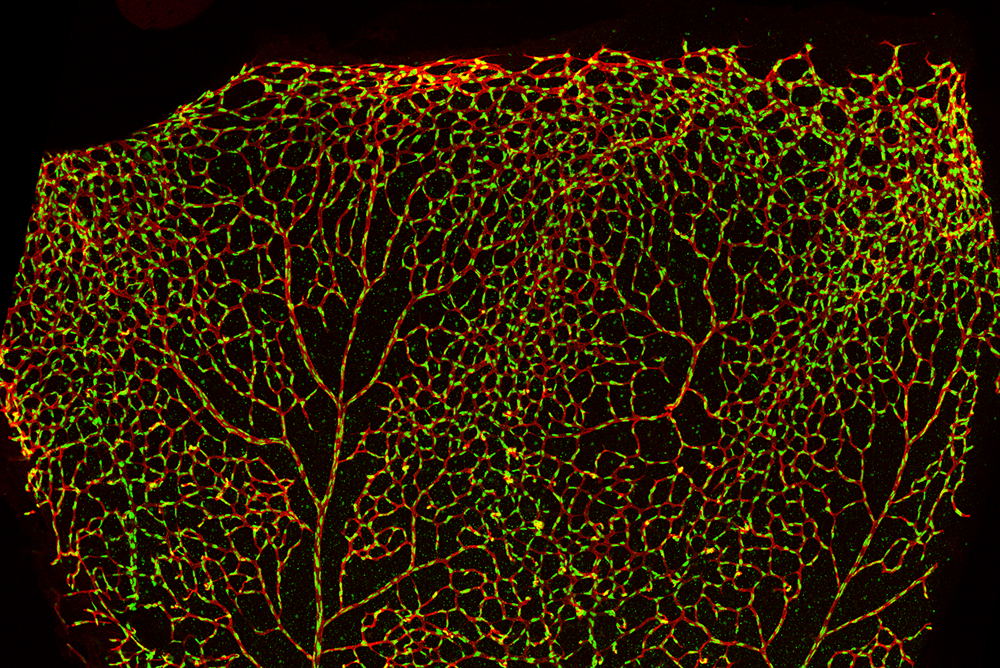
Submitted by: Swathi Ayloo, lab of Chenghua Gu
Winner of 2018 HBI “Beauty of the Brain” Image Contest
The image is a snapshot of the retina early in development, taken from a 1 week old mouse. Shown in red are the blood vessels of the retina and in green are the nuclei of the cells making up the blood vessels. This image captures the highly intricate network of the blood vessels, and the nuclei reveal the dense packing of the cells within the vessels.
The Circle of Willis
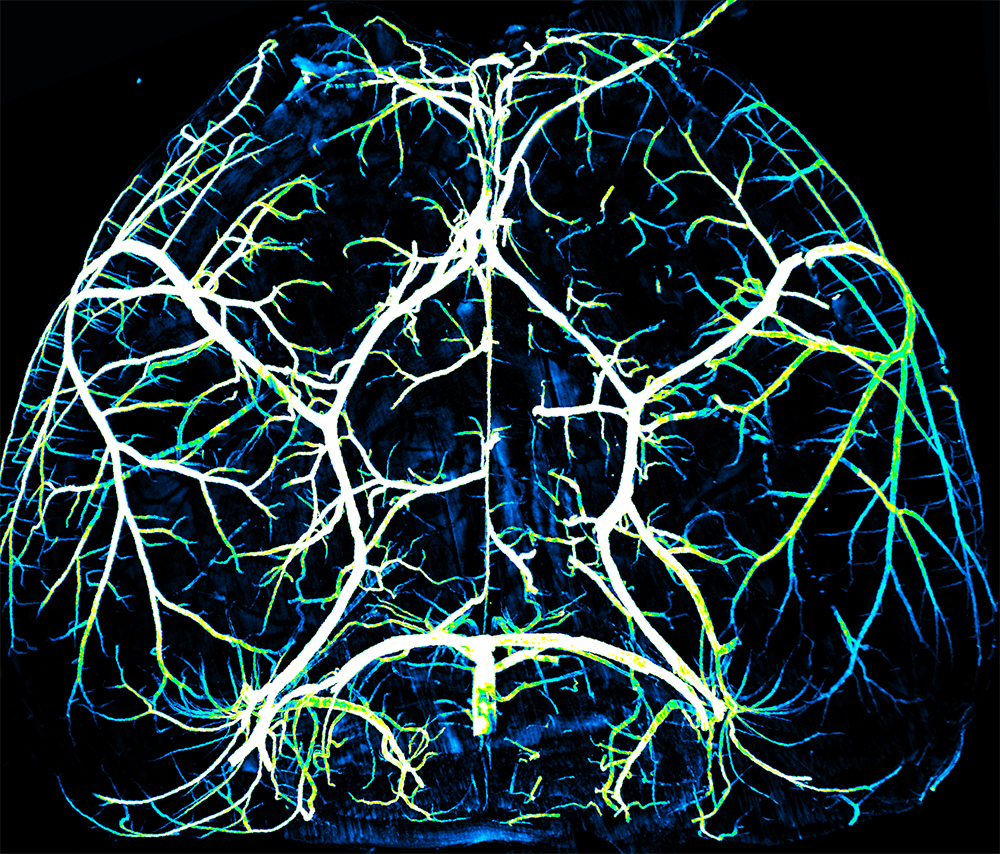
Submitted by: Brian Wai Chow, lab of Chenghua Gu
Winner of 2018 HBI “Beauty of the Brain” Image Contest
The arteries supply nutrients and oxygen to the metabolically demanding brain
Diffusion MRI Tractography of the Human Subcortical Auditory Pathway
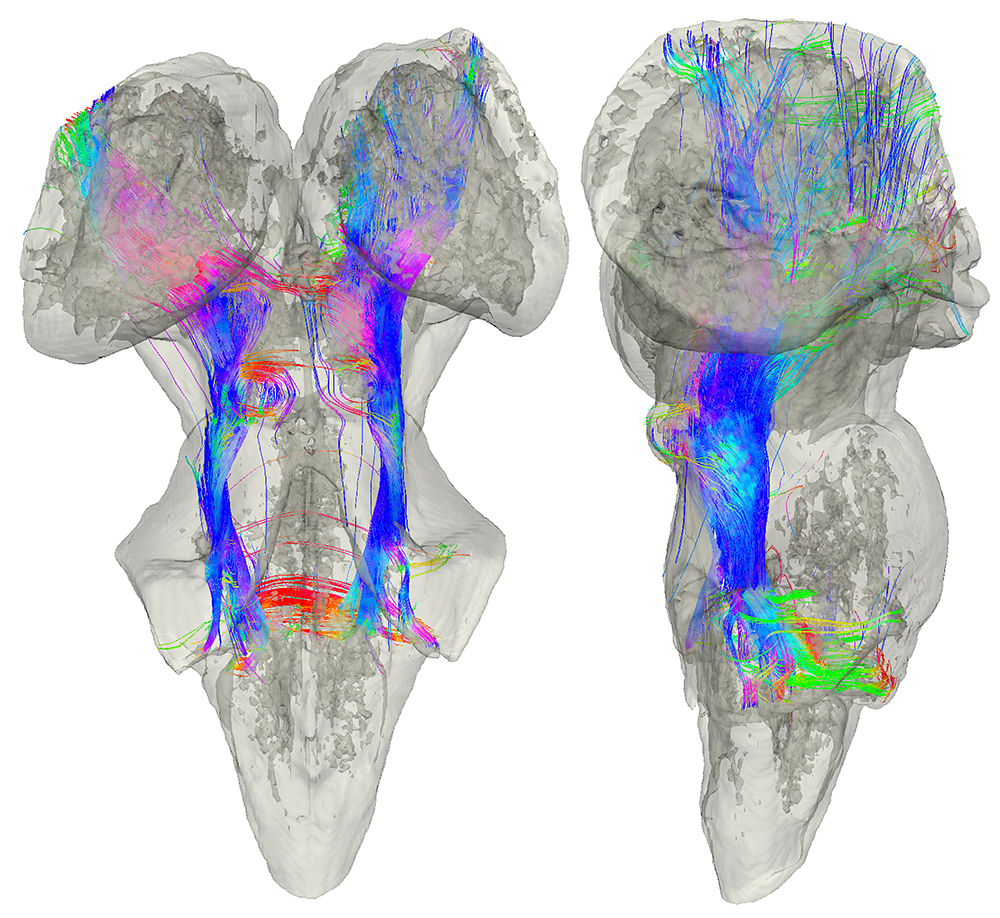
Submitted by: Kevin Sitek, lab of Satrajit Ghosh
Winner of 2018 HBI “Beauty of the Brain” Image Contest
The auditory pathway transmits sound information between the inner ear and the auditory cortex. Using diffusion MRI tractography from a postmortem human brainstem and thalamus, I identified likely white matter connections that swirl into the inferior colliculus, run along the lateral lemniscus, and reach out through the auditory nerve.
Glomeruli of the Fruit Fly Antenna Lobe
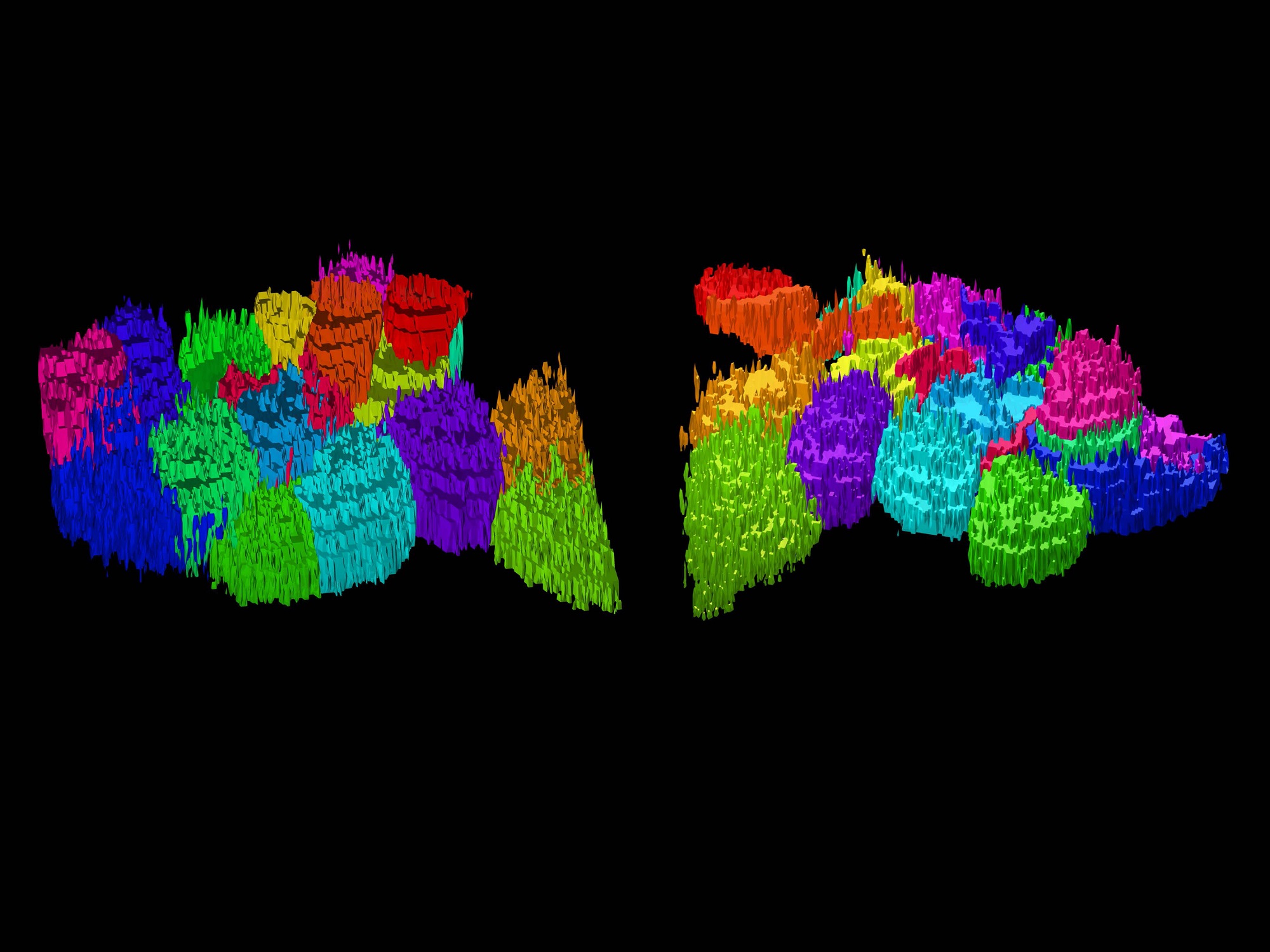
Submitted by: Matthew Churgin, lab of Benjamin de Bivort
This 3-D rendering of a single fruit fly’s antenna lobes, which constitute the first site of odor processing, was acquired using two-photon fluorescence microscopy. Shown are projection neuron dendrites in discrete structures called glomeruli. Each glomerulus relays odor signals from a single odorant receptor to higher brain regions.
All Orientations Welcome
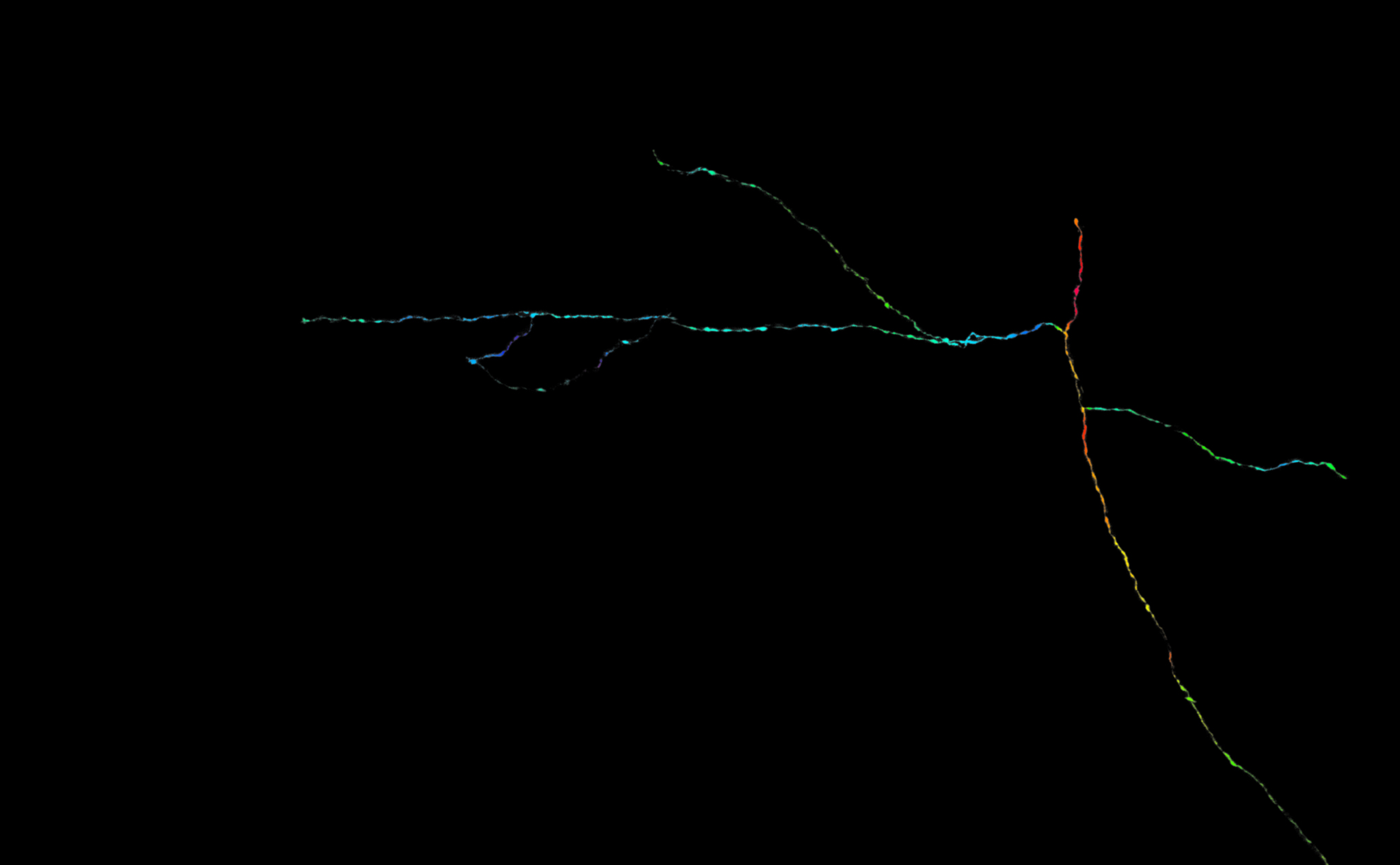
Submitted by: Erin Diel, lab of Takao Hensch
This single axon, reconstructed and filtered from a dense field of thalamocortical axons, is color coded by its underlying branch orientation. Its diverse branches could subserve unique functional contributions, much like the unique perspectives offered by a diverse pool of scientists.
Boosting the Brain: The Choroid Plexus
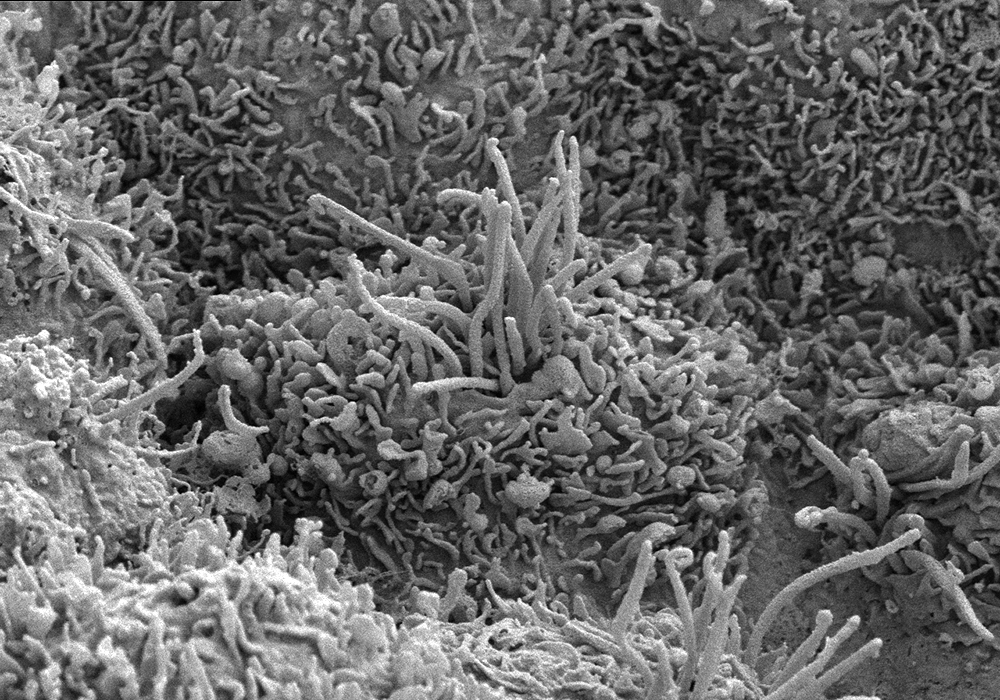

Submitted by: Ryan Fame, lab of Maria Lehtinen
This pillow-like cell is a choroid plexus epithelial cell from a human brain. These cells secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a clear liquid that supports brain health by providing a buoyant cushion, essential nutrients, and a perfect external environment. The long finger-like cilia keep the fluid moving so it stays fresh.
Rendered
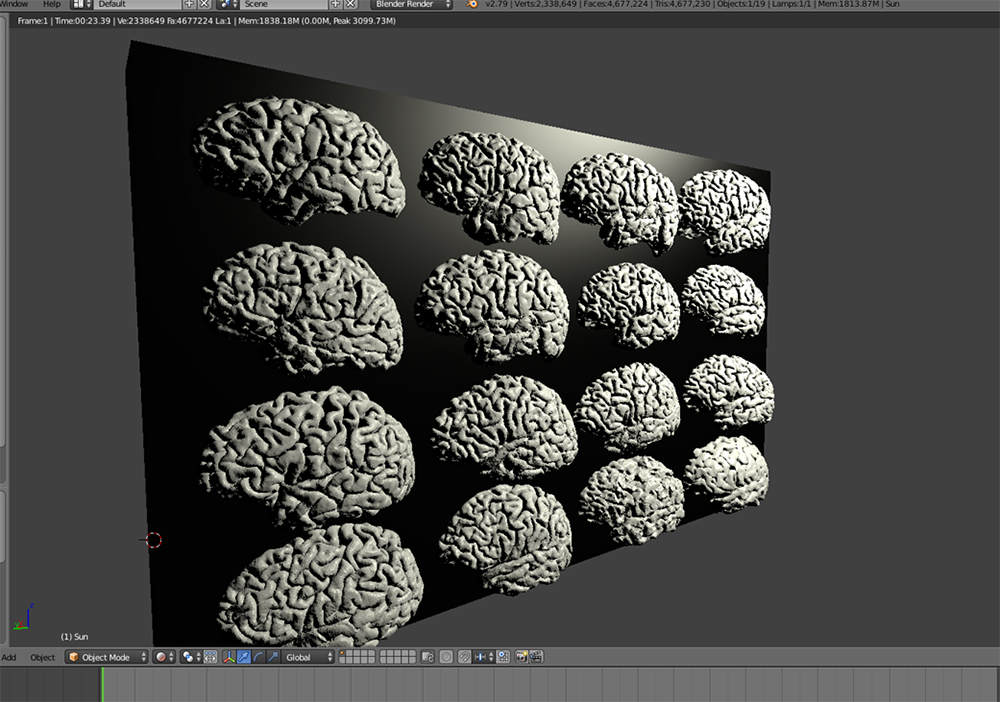
Submitted by: Lynde Folsom, labs of Joshua Buckholtz and Sydney Cash
Using MRI brain scans and 3D printing tools at Massachusetts General Hospital, this sculpture incorporates printed brain renderings and LEDs controlled by a mini-computer. The light patterns represent electrical activity between brain cells, brain regions, and communication between people. Thus demonstrating the rendering of society and creative thought via community.
Neurons Within the Mouse Retina
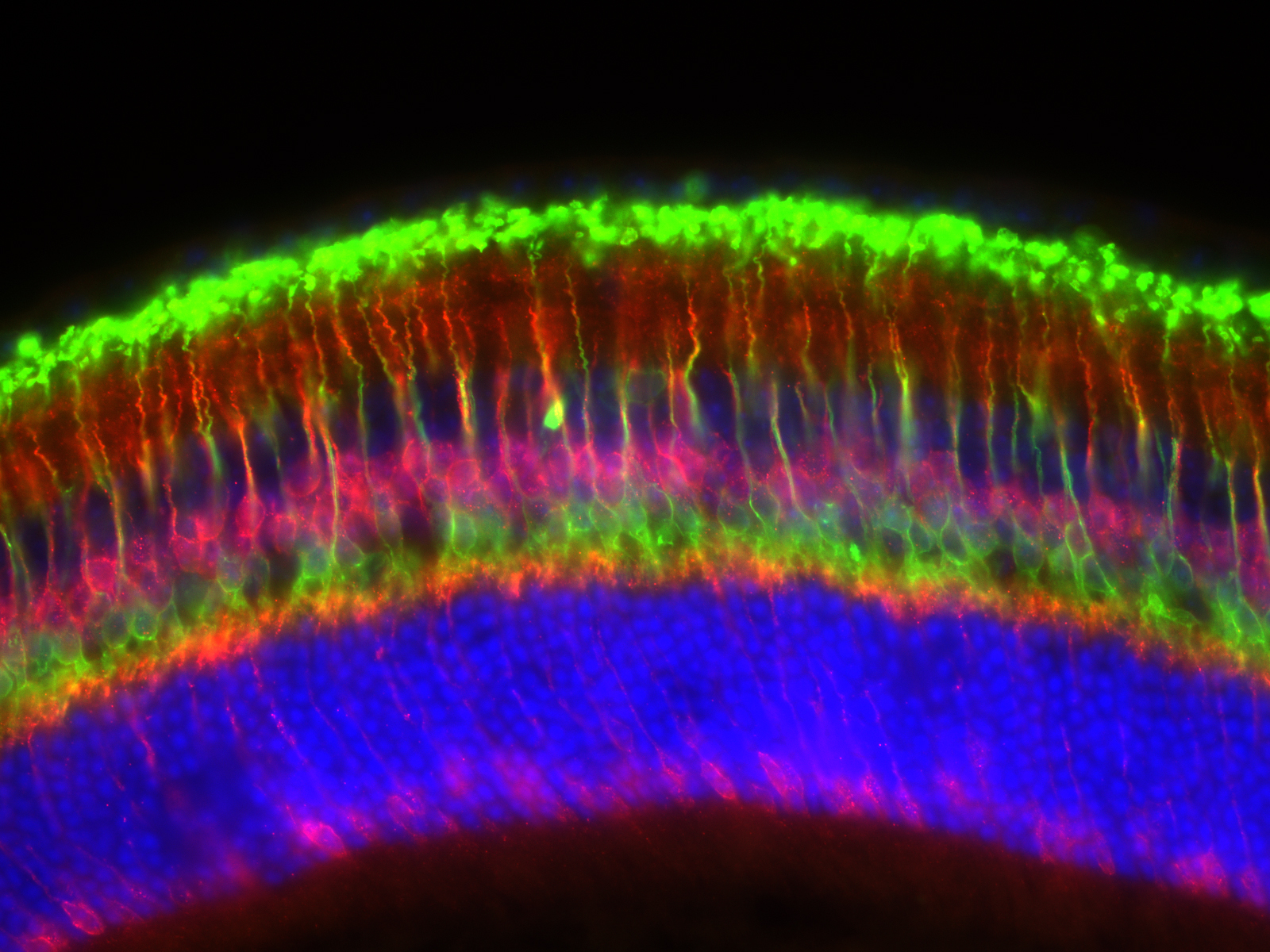
Submitted by: Nicholas Hanovice, lab of Larry Benowitz
Distinct types of retinal neurons labeled with fluorescent markers in a transverse cross-section of an adult mouse retina.
Synaptic Talk Inside Brain
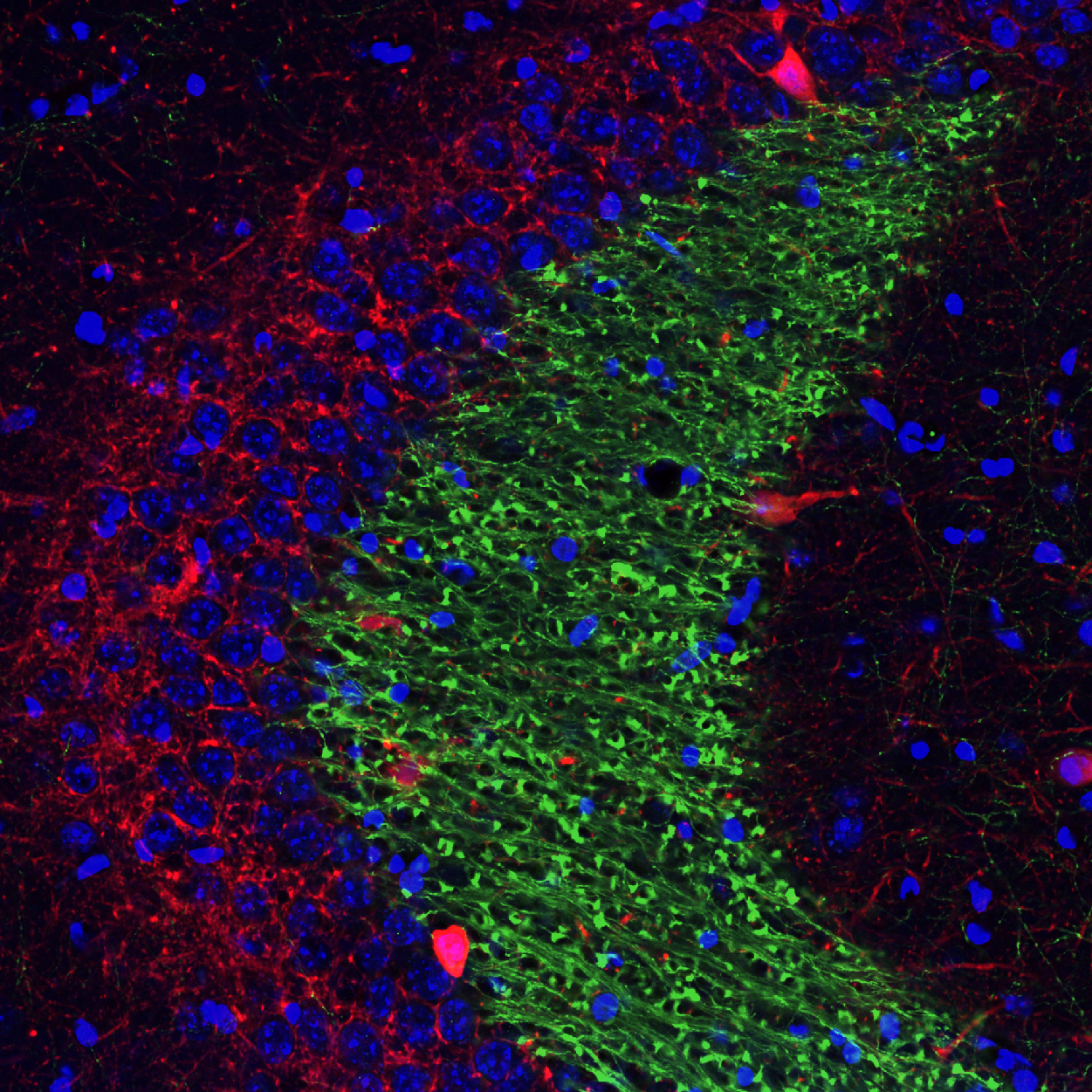
Submitted by: Nannan Guo, lab of Amar Sahay
Mossy fiber terminal (Green) forming multiple synapses with excitatory and inhibitory neurons (red) in CA3 in underlies information flow inside hippocampus.
Man-Made Brain
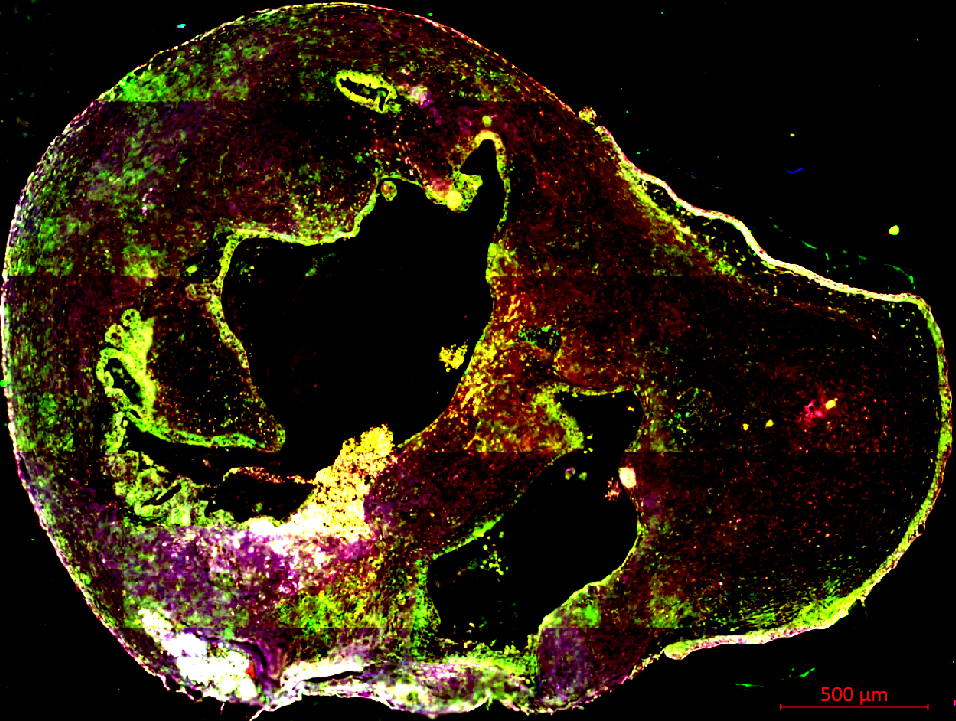
Submitted by: Annie Kathuria, lab of Rakesh Karmacharya
Human stem cell derived brain organoid
Retinofugal Projections into the Optic Tectum of Larval Zebrafish
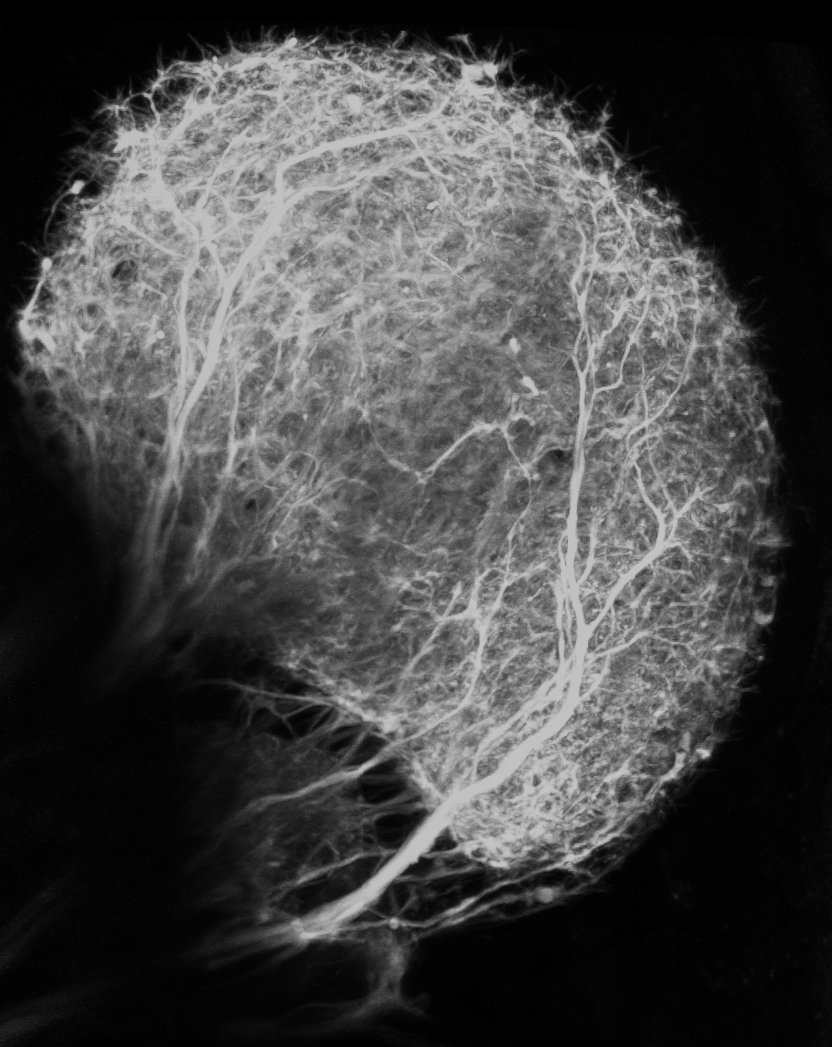
Submitted by: Clemens Riegler, lab of Florian Engert
Retinal Ganglion Cells relay information about the visual world into the brain. The axons of retinal ganglion cells project into the optic tectum thereby creating a visual representation of the environment in the brain with each axon carrying unique visual features.
Staying in Touch
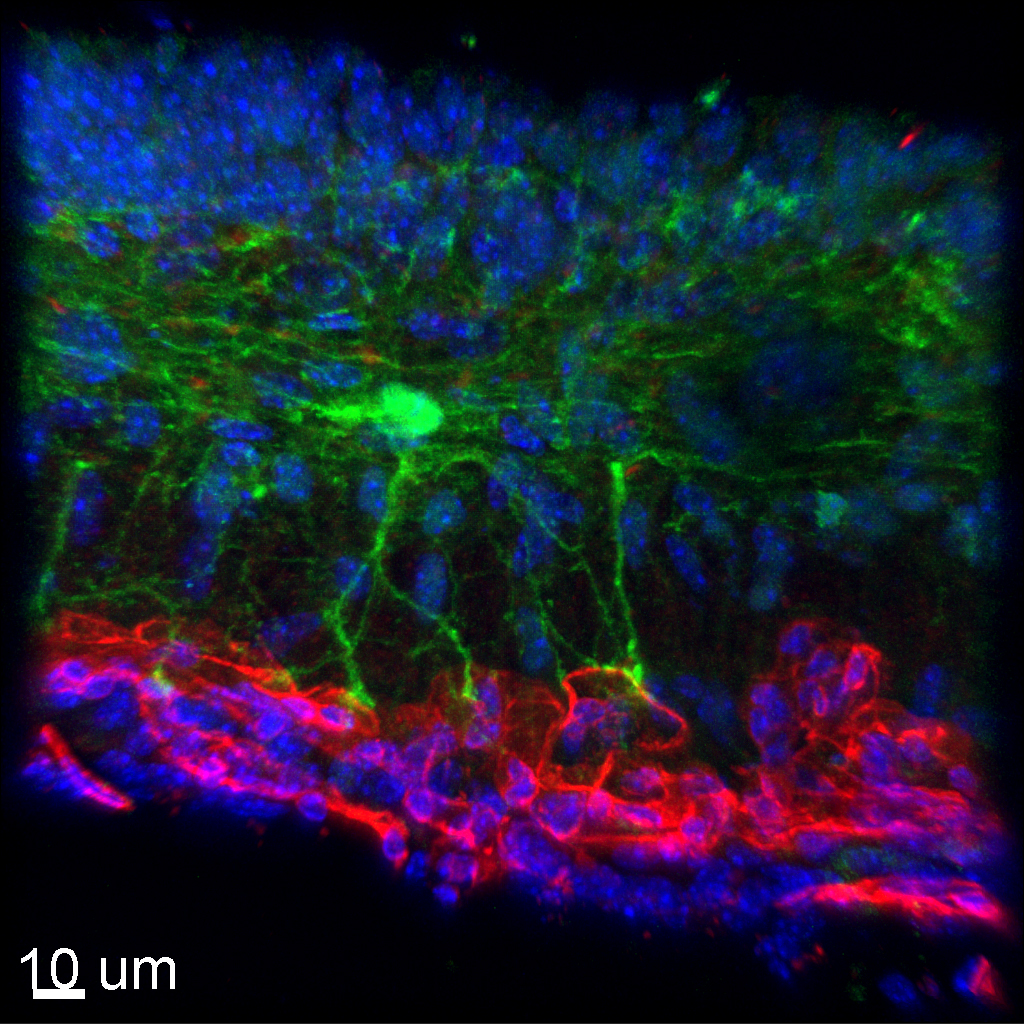
Submitted by: Urs Langen, lab of Chenghua Gu
An astrocyte in contact with a blood vessel in the median eminence of a mouse brain.
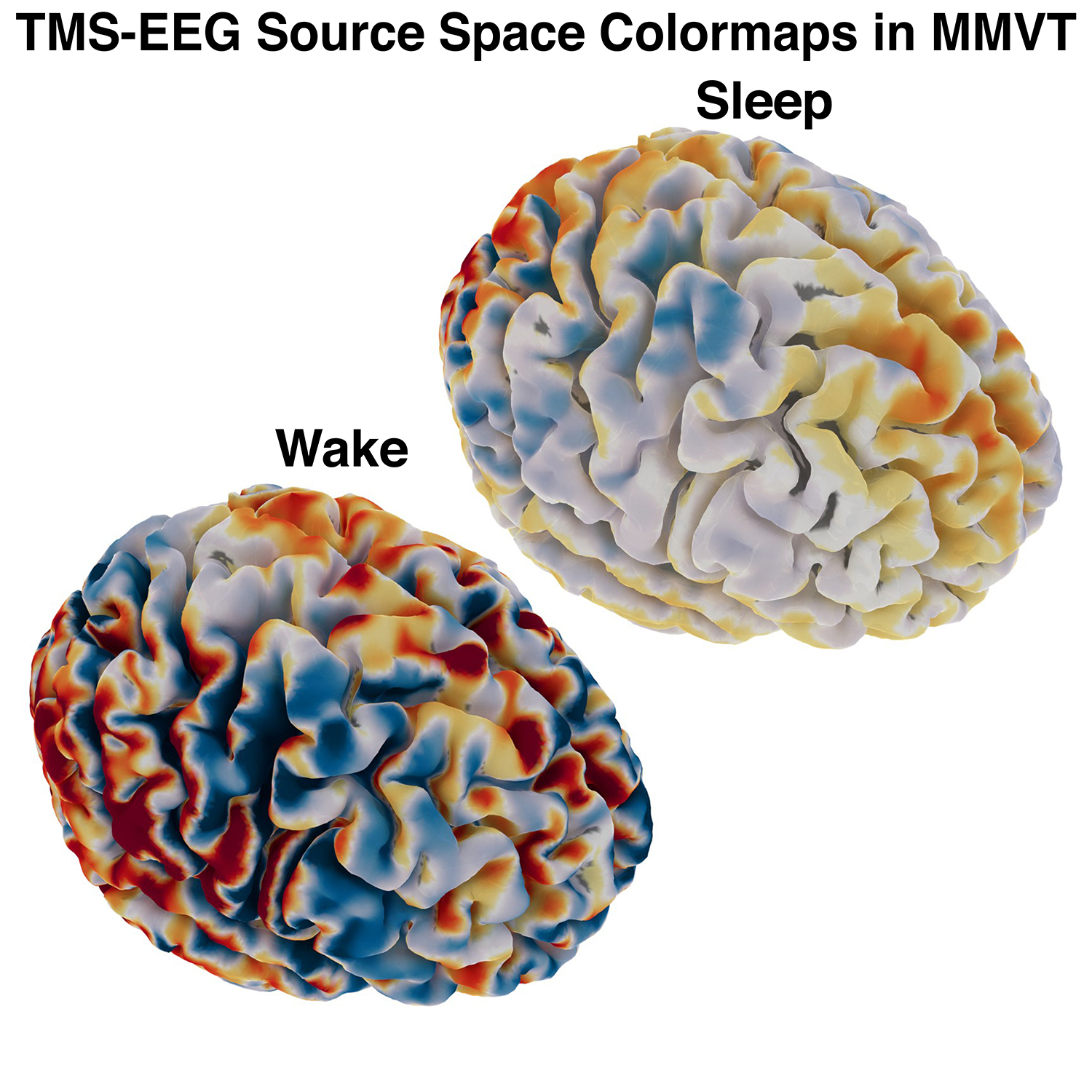
Submitted by: Alexander Rockhill, lab of Alik Widge
While recording a high-density 96 channel EEG and stimulating the pre-motor area with TMS, volunteers took a nap. This image is the brain activity at the surface of the cortex while the volunteers were awake and asleep. Cortical activity was estimated by modeling how current would propagate to the scalp from the brain by reconstructing a head model from a structural MRI.
Neural Stem Cell in the Subgranular Zone of the DG
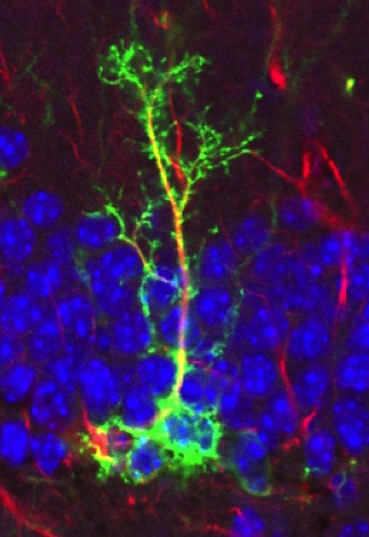
Submitted by: Cinzia Vicidomini, lab of Amar Sahay
Mature Neuron of the DG: “You can be anything you want when you grow up”
Neural Stem cell of the DG: “I want to be a granule cell neuron like you!!”
From Human Adult Fibroblast to CA3 Neuron
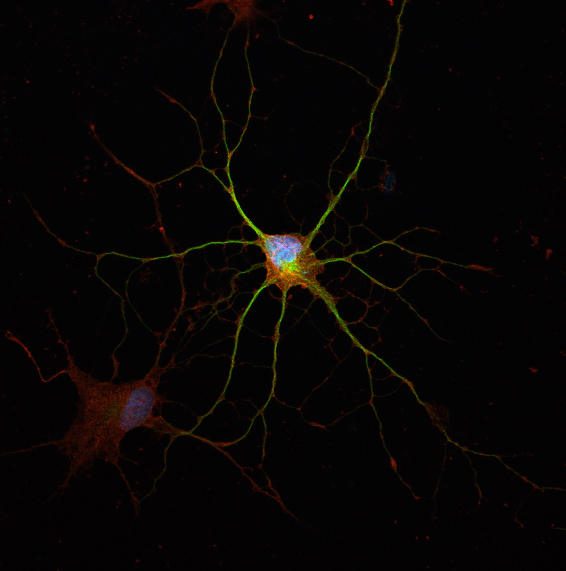
Submitted by: Haley Zanga, lab of Amar Sahay
Where does the fibroblast go when it wants to become a neuron? “transFIBROstation”
Pericellular Basket Surrounds a Cell in the Lateral Septum
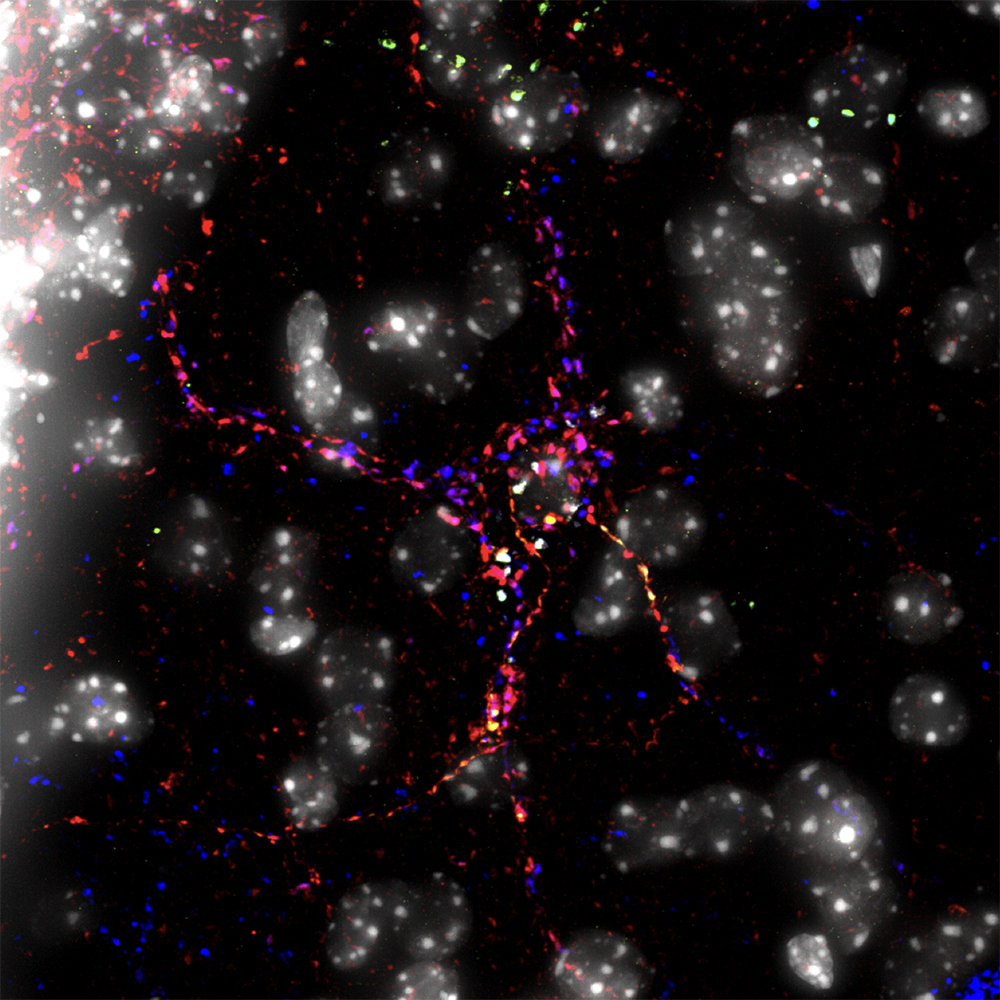
Submitted by: Rebecca Senft, lab of Susan Dymecki
At the image center is a single gray nucleus of a cell that sits within a pericellular basket. The colorful basket around the cell is formed by projections from different neurons, which appear as brightly colored orbs. The different colors of these projections indicate that different neurotransmitters are being released.
Serotonergic Modulation of Sensory Information
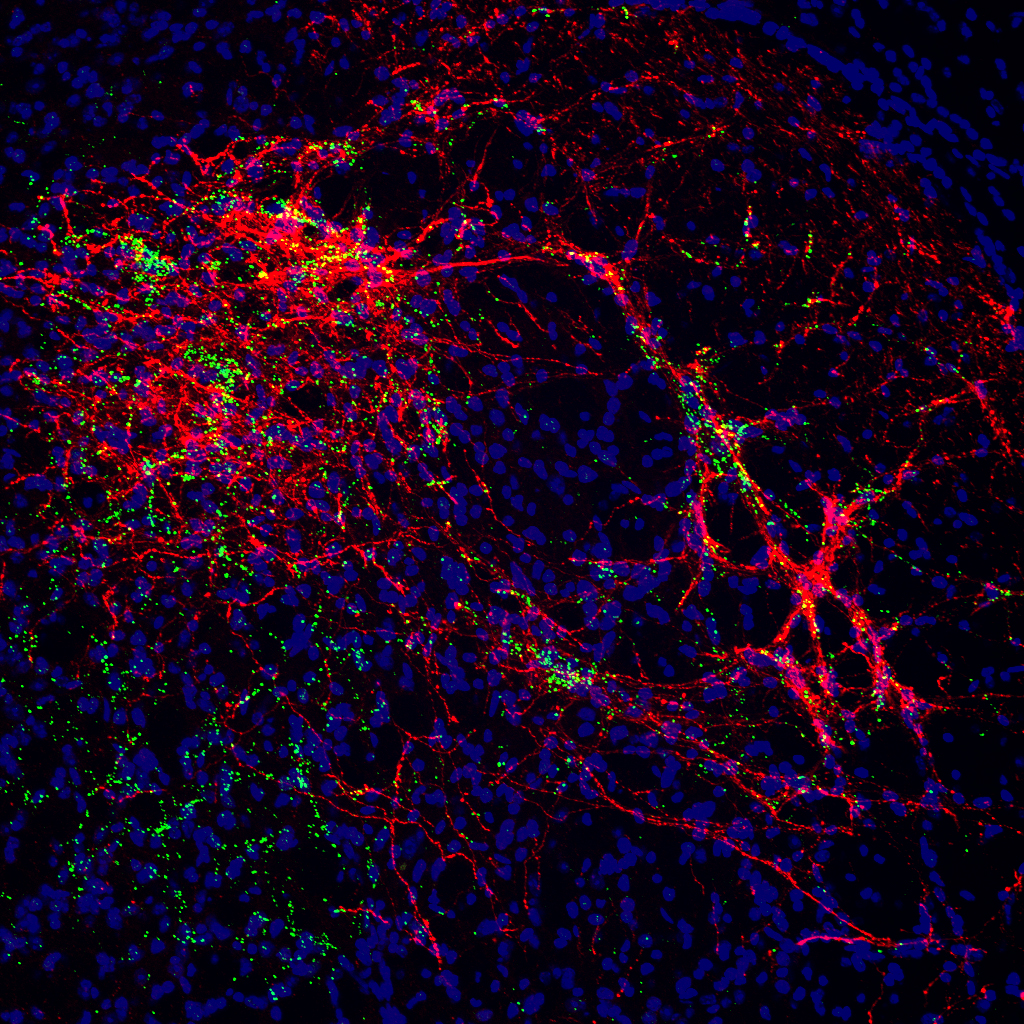
Submitted by: Olga Alekseyenko, lab of Susan Dymecki
Genetically labeled serotonin terminals (synaptotagmin-GFP marker, green) converge on the CGRP-positive (red) afferents of trigeminal sensory neurons in spinal trigeminal nucleus of mouse brainstem. Nuclear marker DAPI is shown in blue.
AH5 Coronal Slice 1127
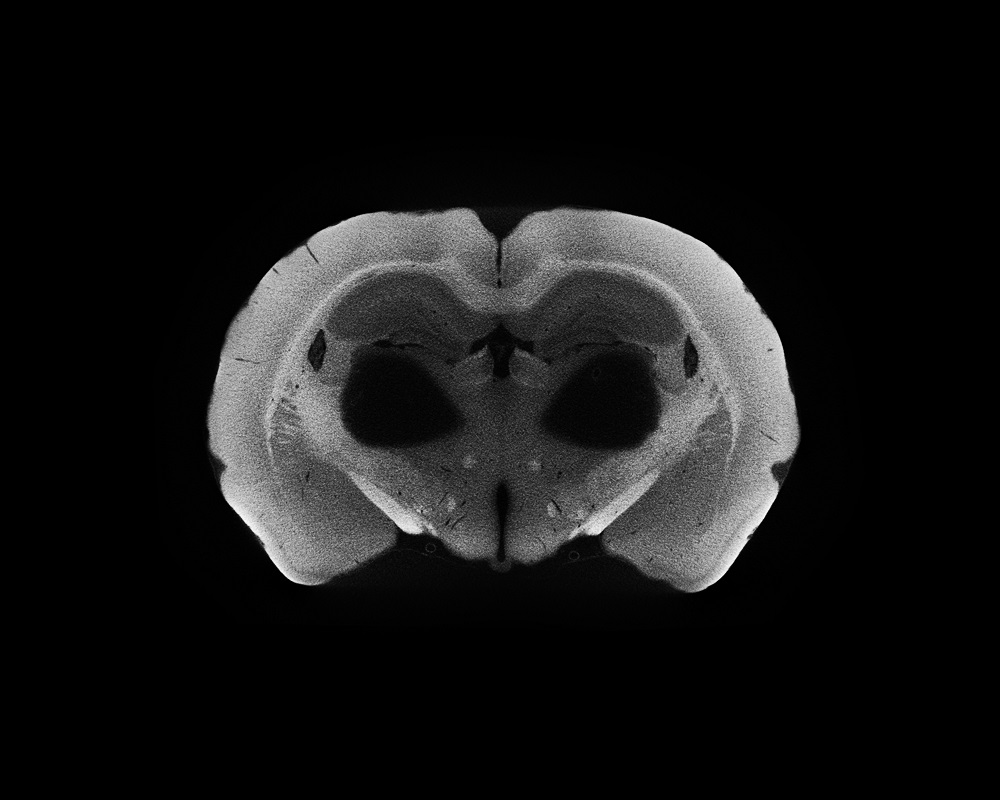
Submitted by: Javier Masis, lab of David Cox
We have an uncanny ability to detect faces, even when there are none. In this image, I discovered a face in a surprisingly appropriate place — the brain. This image was created from a technique that makes a rat brain visible to x-rays using a heavy metal called osmium.
Thoughts and Feelings
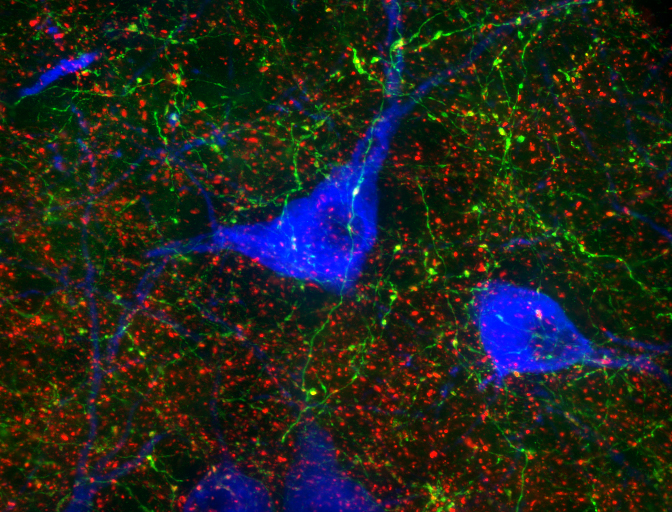
Submitted by: Paul Hatini, lab of Kathryn Commons
Information about conscious thoughts arising in the cortex is passed from the green axons to serotonin neurons, marked in blue. Serotonin neurons use this information, along with information coming from other synapses marked in red, to control mood and motivated behavior.
Human Retinal Organoids to Study the Underlying Causes of Spinocerebellar Ataxia 7
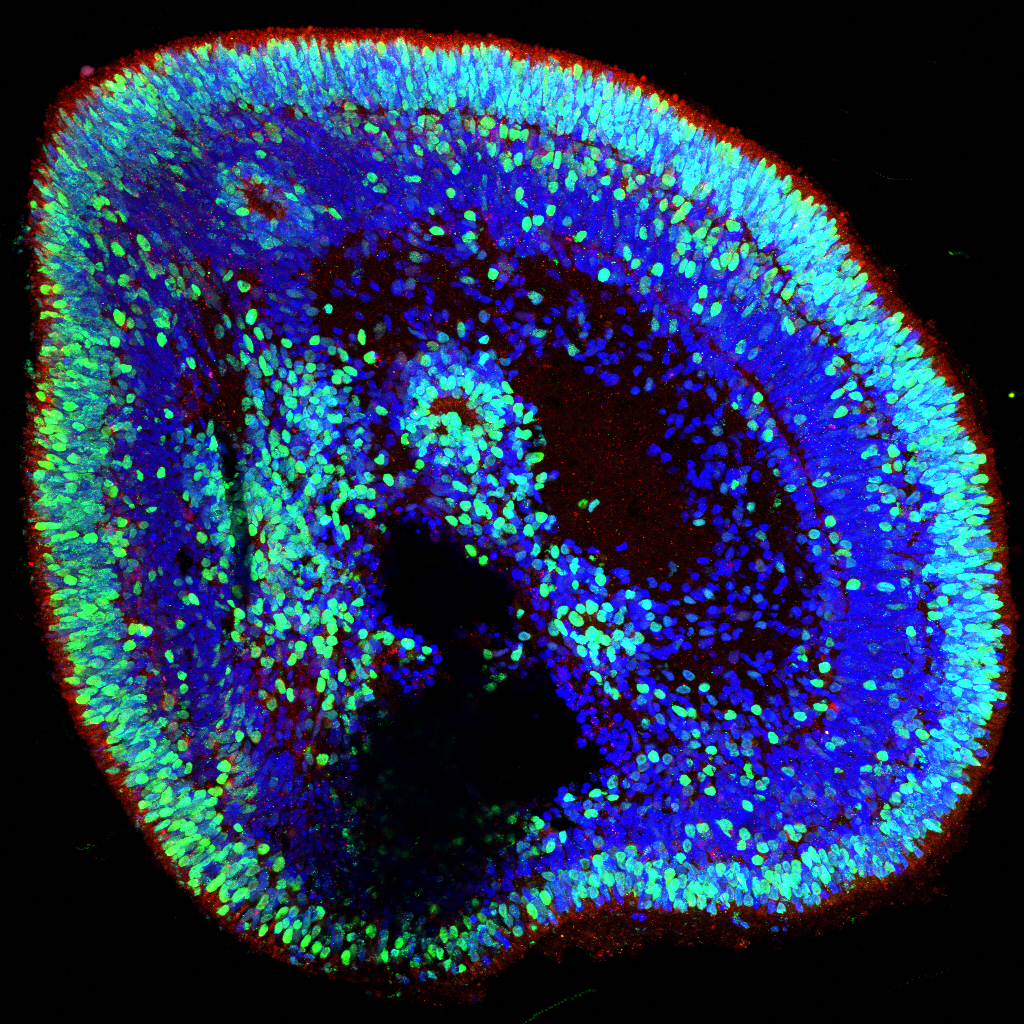
Submitted by: Patrick Ovando-Roche, lab of Vikram Khurana
Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) were generated from a patient suffering from Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 7, a neurodegenerative disease that affects both retina and cerebellum. These cells were stimulated to become retinal organoids to study the disease in the dish. Image shows a highly organized developing photoreceptor cell layer in green color and their outer-segment structures (the structures responsible for harnessing light and converting it into vision) in red. The cell nuclei of all cells is shown in blue.
