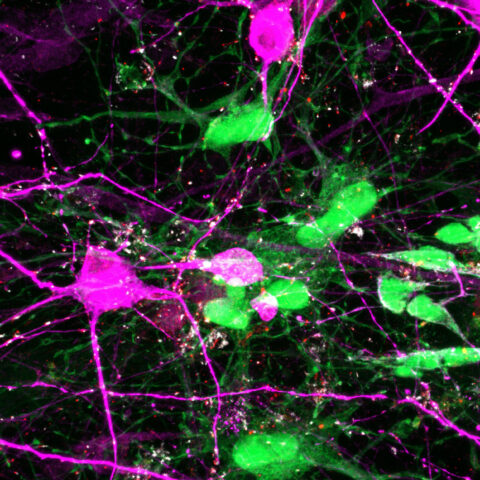
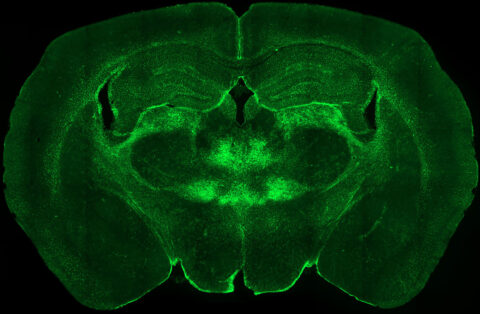
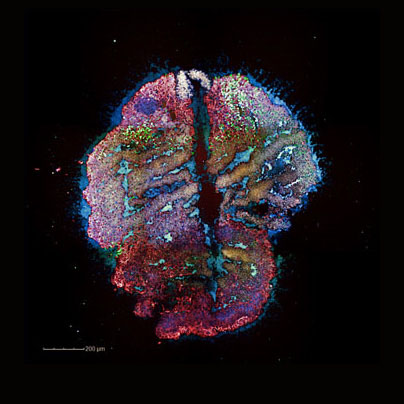
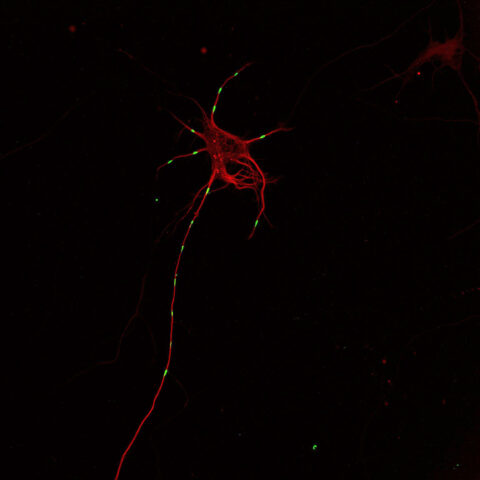
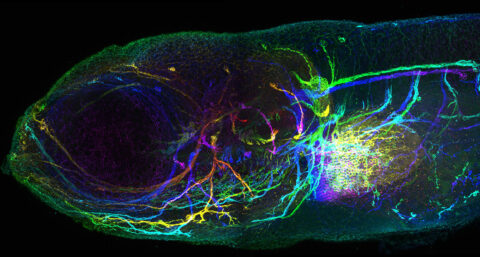
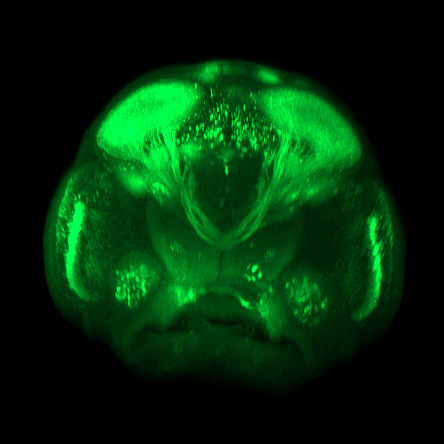
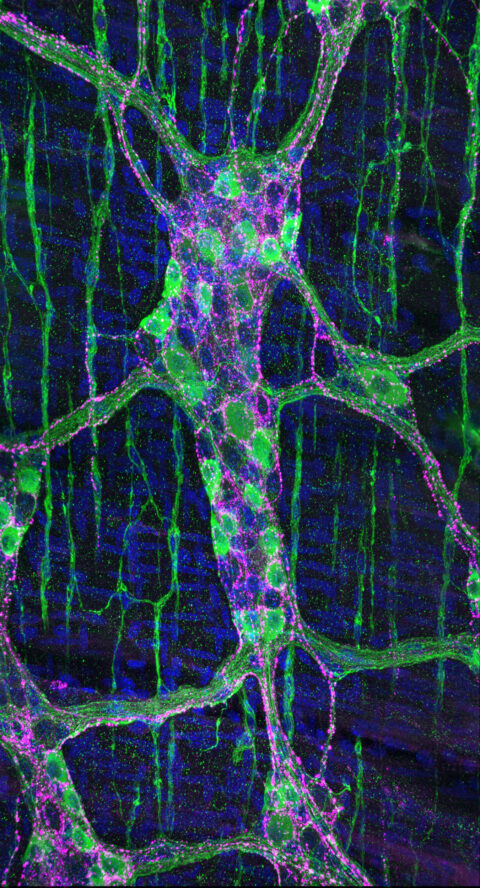
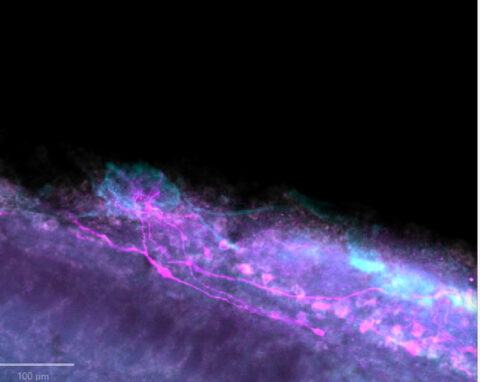
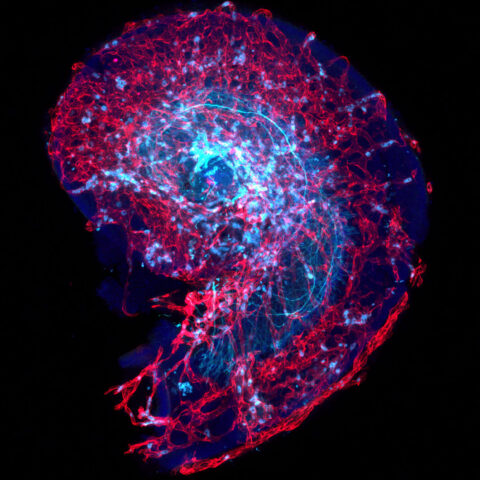
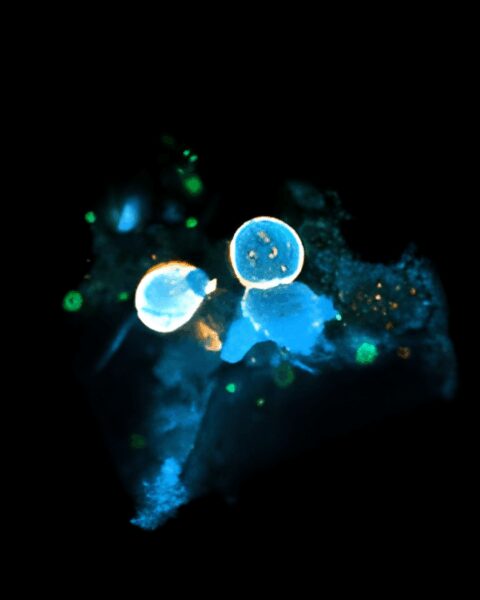
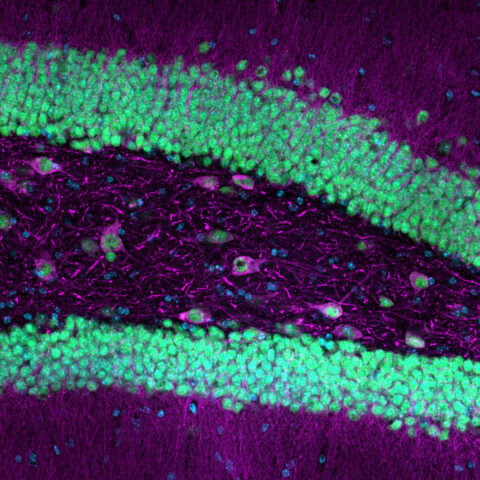
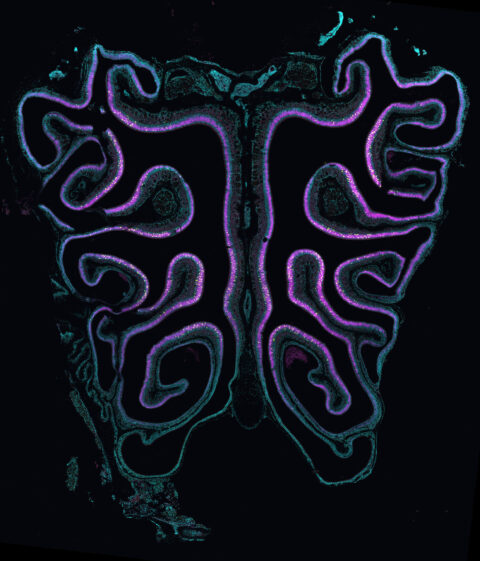
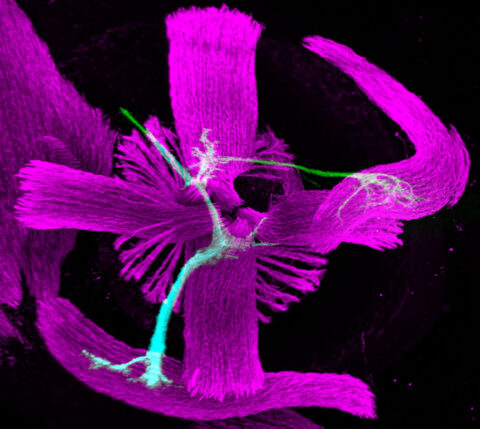
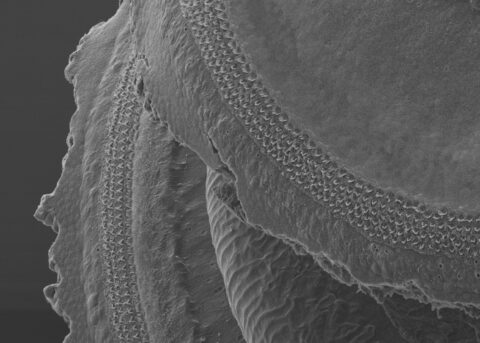
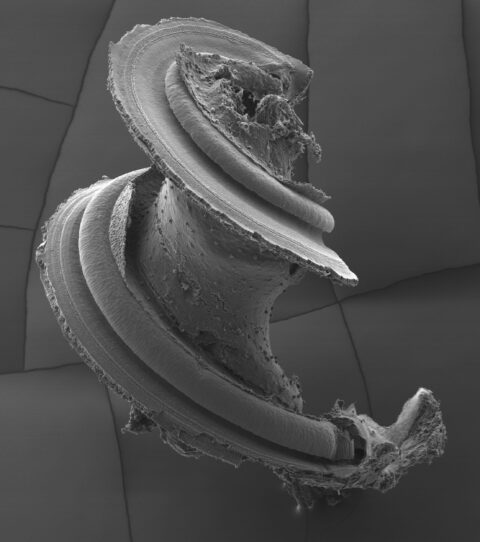
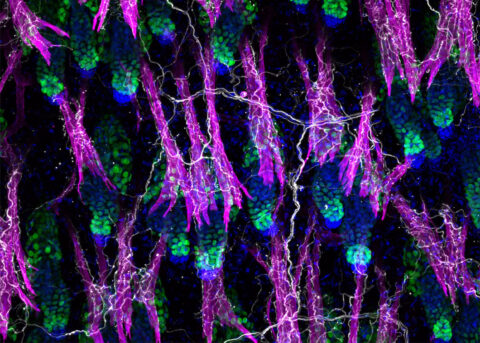
Beauty of the Brain
Each year, we sponsor an image contest where Harvard neuroscientists can share their amazing research images with the world. Below you will find all entries to our contest dating back to 2017. You can filter the contest by year by clicking the relevant heading. We typically solicit new images in the fall semester; join our mailing list to make sure you don’t miss out!